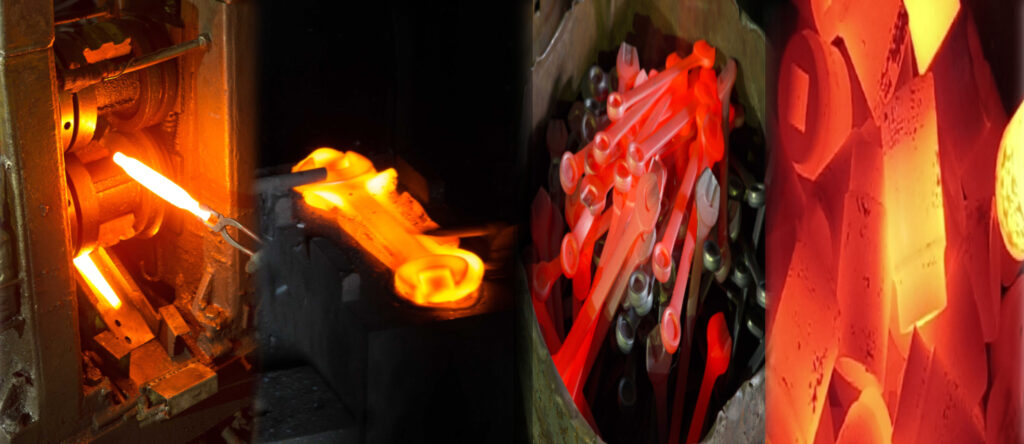
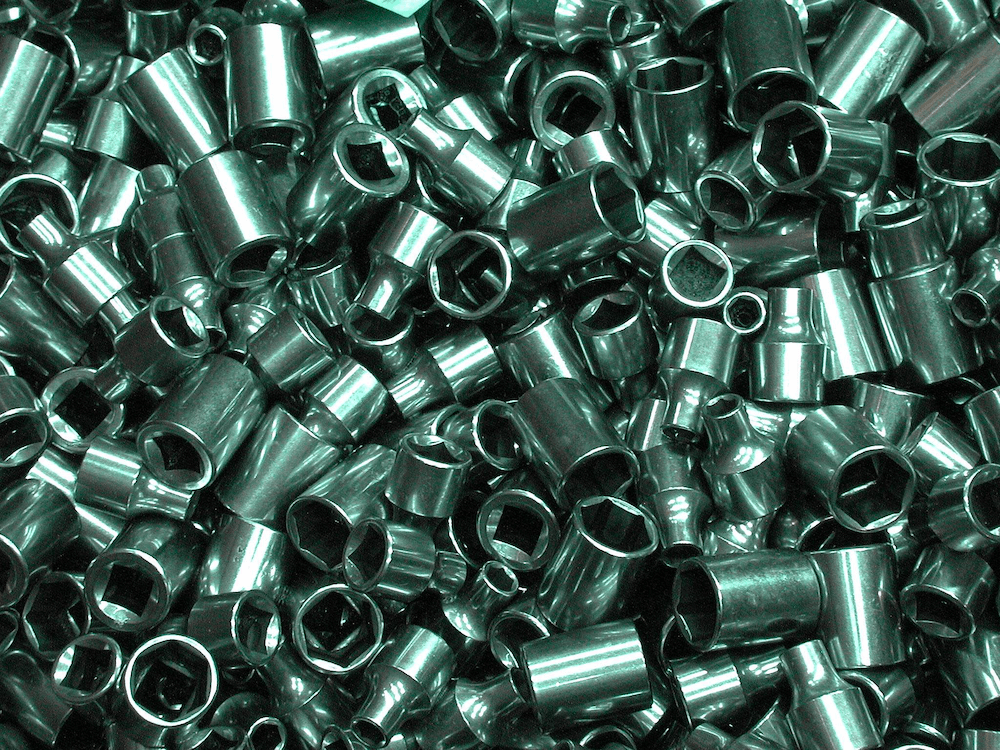
The surface finish of a tool can have a major impact on the quality of the coating. To ensure optimal performance, it is important to use the appropriate finishing technique when preparing the surface.
- For socket and steel made tools, this means using
- chrome plating,
- burnishing or polishing to create a smooth,
- evenly finished surface. Any microcracks, oxide layers or rehardening zones should be removed, and care should be taken to avoid blunt grinding wheels which can damage the tool.
- Cutting edges should be burr-free for best results. Once the surface is prepped, it is important to remove any residual polishing compounds before applying the coating.
Liquid Nitriding
Parts and components can be hardened through thermo-chemical diffusion treatment, providing repeatable results. This process is carried out at critical temperatures in order to preserve dimensional stability, as well as providing corrosion protection and long-term resistance to wear, seizure, scuffing, adhesion and fatigue.

What are the causes of micro cracking? Micro-fractures, also known as micro-cracks, can occur in solar cells as a form of degradation. The silicon used in solar cells is very thin, and expands and contracts with changes in temperature. So, during the day when it’s hotter out, the solar panels expand. And then at night, when it’s cooler, they contract. This thermal cycling can cause micro-cracks to form over time.

t. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
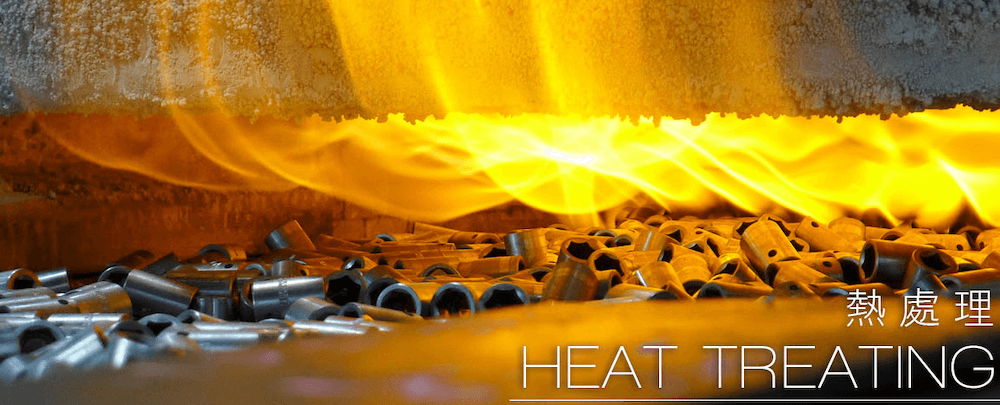

Heat treatment is the use of extreme temperatures to achieve a desired result. It is used in variety of industries on different types of materials, such as metals and alloys. Heat treatments are applied for several reasons and include carburizing, strengthening through precipitation hardening, recovering from prior stress relief or quenching and normalizing.
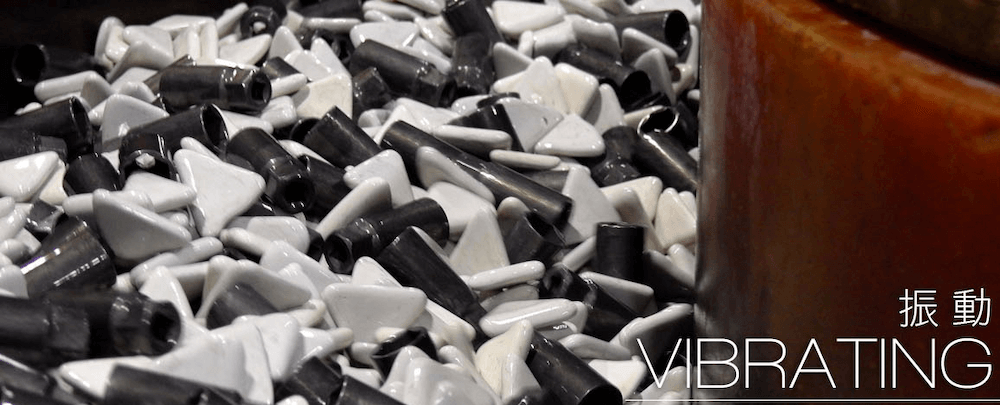


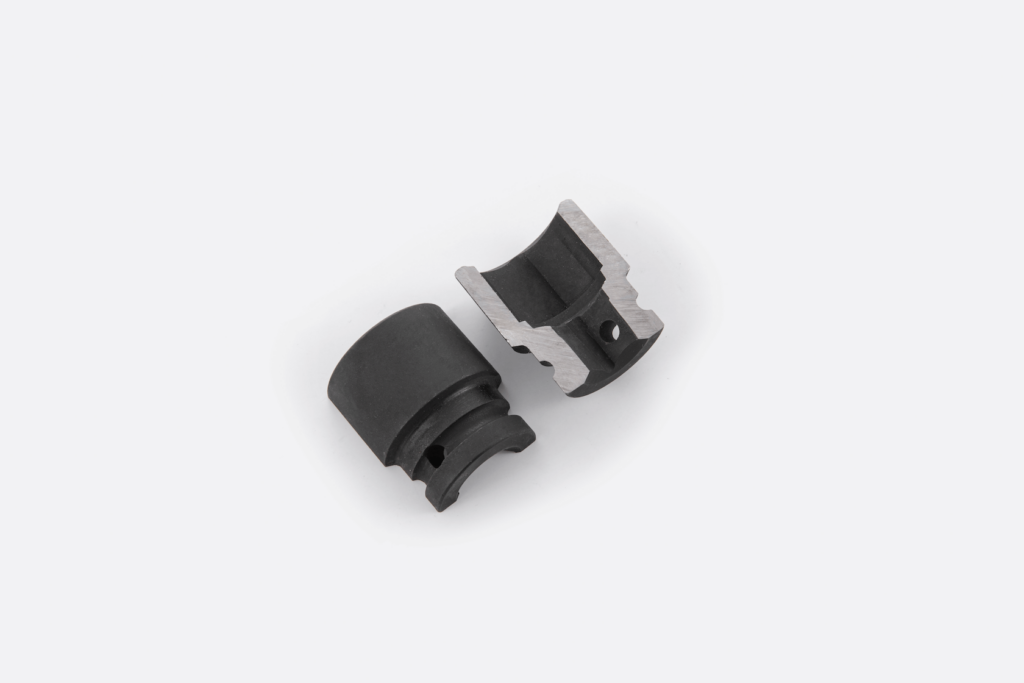
Vibration-machining is a process in which an abrasive material acts on the workpiece. This method is used to realize: – Blunt edges and pointed tips – Glossy finishes – Great surface preparation of metal elements for galvanic coatings – Uniformity of the structure across different parts of the
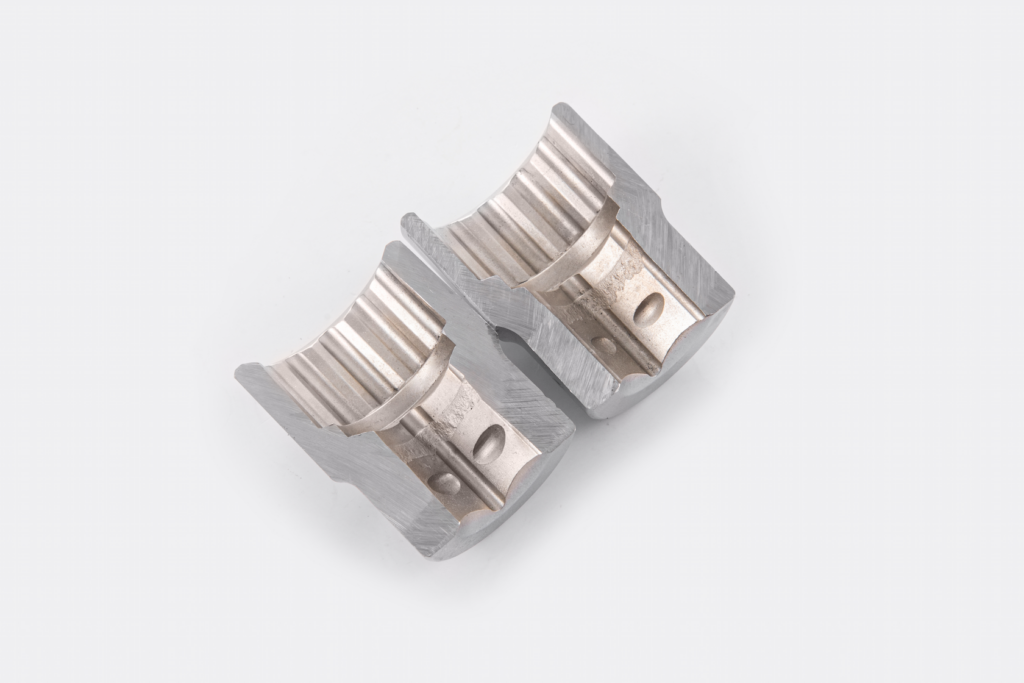


What is surface roughness?
The surface of any machined part has a complex structure made up of bumps and indentations of different sizes, depths and spacing; and the so-called surface roughness refers to the smaller indentations that form on the surface. Products like packaging or car gauges and panels go through a machining process that leaves behind a “smooth and shiny” or “rough and dull” appearance, depending on the surface roughness.
ISO 25178 surface topography (surface roughness measurement) is an international standard for evaluating surface roughness. The JIS B 0671-1/ ISO 13565-1 (line roughness measurement) specification is based on the assessment of probe type roughness, while ISO 25178 surface topography supports both “contact (probe)
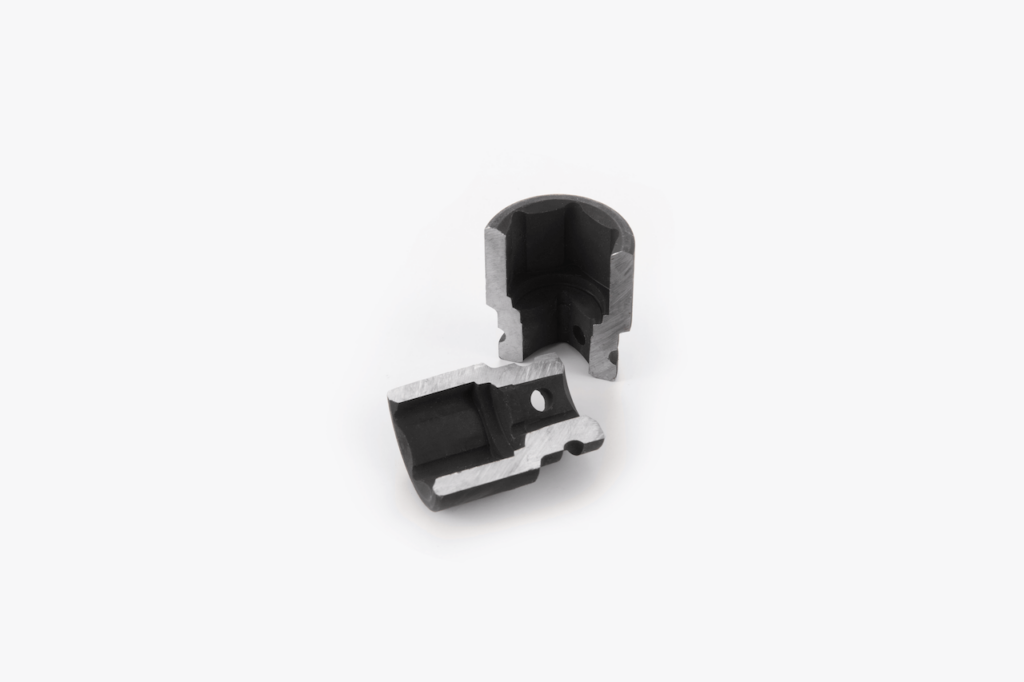
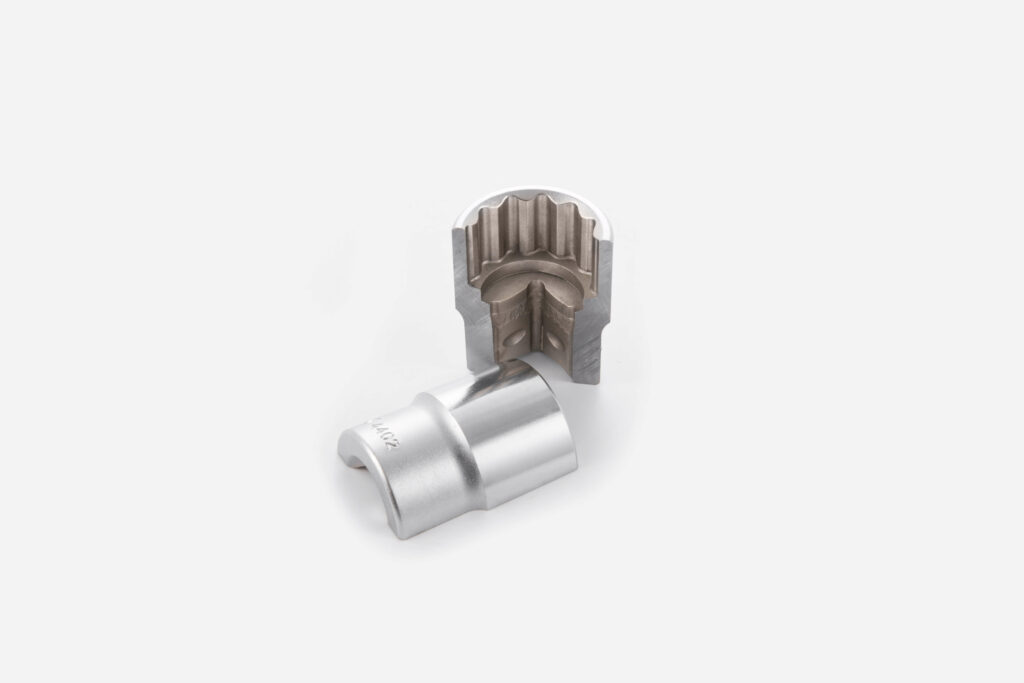



In this section, the different surface roughness scales used in manufacturing processes. For example, Ra represents roughness average, an important measurement for texture surfaces. Rt= Roughness Total.
Production line tools such as lathes and millers measure the RMS (root mean square) of a surface to determine how close its peaks are to one another. In order to make a quantitative evaluation, workers need instruments like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical correlators. Tools like these allow manufacturers to adjust their CNC machines over time to keep improving quality control standards and productivity.

